
Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing areas of computer careers out there. As more and more of our world migrates online, to cloud applications and with online businesses, cybersecurity knowledge is increasingly important. Companies need their IT staff to have at least a basic understanding of the precepts of cybersecurity, and the demand for experts in the field is steadily increasing. Every year, new high-level attacks and data breaches showcase just how important this security knowledge is.
As a school offering a cybersecurity program, we are asked a lot of different questions about the industry. We’ve compiled the most common questions and their answers below.
Question: Can a Cybersecurity Certification Help Me Get a Job?
Yes! While the industry of cybersecurity is full of people with no formal education and people who have learned on the job, it is quickly becoming a formalized career path. Higher education in cybersecurity can help you land a job, and a certification from one of the primary certificate authorities is meaningful.

With a college degree, you never know how much it’s going to help you land a job. Employers have to be familiar with the school and the program to know whether or not the degree is a meaningless piece of paper. With certificates, employers know that a prospective employee has the knowledge they claim because they passed the industry-standard testing to earn it. Certificates are highly meaningful, and employers know what to look for.
A cybersecurity certificate can move your resume from the middle of the pack to the top of the shortlist. Earn yours starting today!
Question: Is Cybersecurity a Good Career Path?
Yes! Cybersecurity is a broad field, with a wide range of possible specialties. If you’re interested in information technology or information security, you can find a career path that suits your desires. You can play defense, protecting a company from potential and actual cybersecurity threats. You can play offense, as an ethical hacker searching for vulnerabilities and informing companies how to fix them, or as a “red team” penetration tester, simulating cybersecurity attacks to demonstrate possible threats.

Cybersecurity is not just a good career path; it’s growing. Every company today needs to pay attention to cybersecurity if they hope to do business. You can use a cybersecurity certificate to get a job anywhere you want, in any industry. You can use it as a bonus for an IT role focused on networking or administration, or you can specialize in cybersecurity and become an on-staff expert, consultant, or even start a security firm of your own. The options are limitless!
Question: What Are the Best Cybersecurity Certifications?
There are dozens of different cybersecurity certificates out there, so it may be difficult to figure out which are the best. Broadly, you can categorize cybersecurity certificates into a handful of groups.
Generalist certificates are certificates that test your general knowledge of cybersecurity. These certificates are broadly recognized but do not indicate a specialty in cybersecurity. They’re best for students who want to pursue a career in IT without being a cybersecurity expert, and include certificates like the ISACA CISM (Certified Information Systems Manager) and the Cisco CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate).
Specialist certificates are certificates that test specific knowledge of the arena of cybersecurity. They’re best for people who want to specialize in cybersecurity, and who want to have jobs as defensive security experts or offensive security consultants. They include certificates such as the CompTIA Security+ and the EC Council CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker).

Generally, the more recognized a certificate, the better it is for your career prospects. The EC-Council, CompTIA, Cisco, (ISC)2, and ISACA are all high-quality certificate authorities, and any certificate they offer will be valuable.
Question: Do I Need a Certification to Get a Job in Cybersecurity?
Not always, but it can certainly help you stand out. Think of it this way; an employer has to hire someone. If they have a pile of 100 resumes, and five people on that list have cybersecurity certificates, those five people are going to be on the shortlist for interviews. A certificate is an indication of your knowledge and experience, and it’s a tangible benefit to your job prospects.
Digital and information security does not require certificates to get a job but you’re more likely to get a job and more likely to start with a higher-tier role with better pay and better job prospects (if you have a certificate relevant to your field).
Question: What Are the Different Kinds of Cybersecurity?
Generally, you can divide cybersecurity into three categories.
The first category is incidental. Many careers in IT currently can benefit from knowledge in cybersecurity. Developers can help build security into the foundation of their code. Network administrators can understand how to help protect their networks from intrusion. Even customer support and help desk roles can benefit from recognizing common signs of cybersecurity threats.

The second category is defensive. Most companies need at least one defensive cybersecurity expert on hand, either on staff or as a company they hire on a contract. A defensive cybersecurity expert can help protect a company against threats and intrusion, both wide-spectrum and targeted. They can help harden a network against threats, and security information and processes from hackers and other threats.

The third category is offensive, or proactive security. Penetration testers, ethical hackers, simulated attackers, and auditors are all offensive security applications. If you’re interested in attempting to hack a company for their benefit, an offensive security role is for you. These employees help show companies how vulnerable their networks are, and work to help them protect themselves.

There’s a lot of overlap between these categories, and it’s entirely possible to move from one to another throughout your career. Cybersecurity knowledge is valuable no matter what career path you take.
Question: How Much Can I Make as a Cybersecurity Expert?
It depends! According to the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics, the 2019 media salary for a cybersecurity expert is $99,730 per year. This increases every year.
Entry-level cybersecurity IT workers can earn anywhere from $55,000 to $80,000 per year. Mid-level cybersecurity experts can earn between $75,000 and $100,000 per year. Upper-level cybersecurity experts can make $150,000 per year or more!
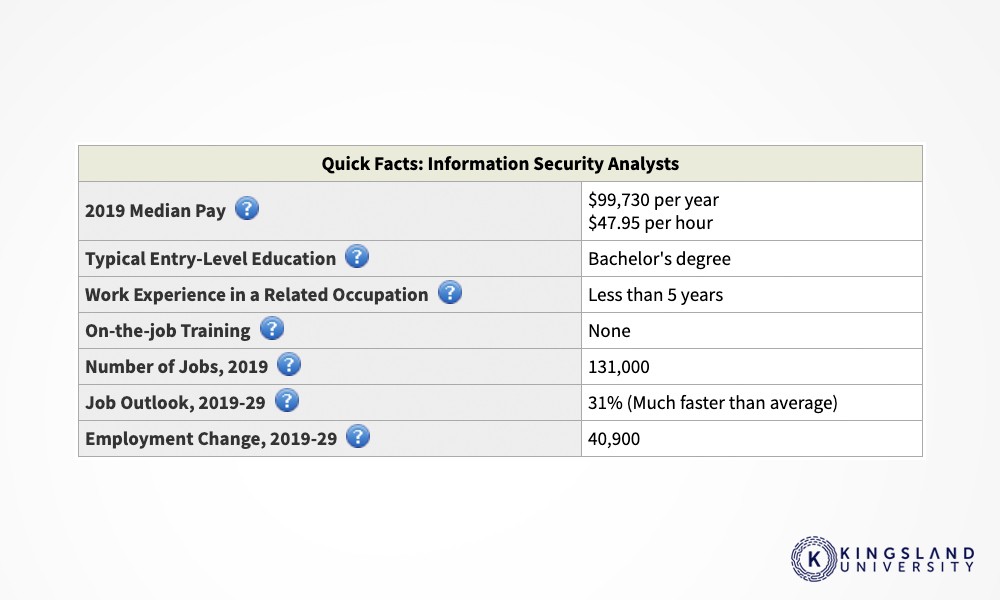
On top of this, job prospects are looking up. The BLS estimates that there are over 500,000 unfilled job openings in cybersecurity, and the field is expected to grow by 30-35% year over year. Job prospects are high and the field is quickly growing, so this is an excellent time to earn your education and enter the exciting field of cybersecurity.
Question: Will a Cybersecurity Certification Increase My Salary?
Yes! If you’re interested in cybersecurity, earning a certificate is tangible value. Employers look for certificates when they hire new employees, and those certificates give you a better position to negotiate your salary. Moreover, if you’re already employed in an Information Technology role, earning a cybersecurity certificate gives you grounds to negotiate a raise. Some companies even have a built-in process to increase salary when an employee earns a new certificate.
According to Hacker News, certificates are very important.
“Across the board, certifications can help boost your yearly salary by 5% to 25% — a huge difference if you can compound that difference across your career. Getting a CISM, CISSP, CISA, or CEH certification can help your cybersecurity career immensely.”
A certification helps you start at a higher base salary, gives you leverage to negotiate a higher salary moving forward, and allows you to grow ever higher as you progress through your career. Additionally, experience plus a certificate allows you the freedom to start a cybersecurity company if you’re inclined to do so.
Question: Do I Need a Cybersecurity Certification to Get a Job in Tech?
No, but it helps! In the past, tech jobs were easy to find even if you had no formal education. We’ve all read stories about industry greats like Bill Gates, Steve Jobs, Mark Zuckerberg, and Jack Dorsey, who dropped out of college to pursue careers in computer science that led to incredible wealth and success. Unfortunately, these are legends from the “wild west” of computer science.
Modern information technology careers can still be found if you have no formal education, but they start as drudgery and require years of work to grow. A bachelor’s degree is required for many IT roles today, and that includes many entry-level starts.

Certifications in cybersecurity serve two roles. First, they demonstrate that you know what you’re doing and you’ve passed tests to prove it. This allows companies to have more confidence in you when they’re considering hiring you or promoting you. Even entry-level jobs, with a certification, are going to start at higher pay and with higher responsibilities.
Second, certifications are an excellent platform for growth. No matter where you are in your career path – new student, returning student, or someone currently employed in the field – earning a certificate allows you to start and grow from a higher position than you otherwise would be able to. Your job prospects will increase, your salary will be higher, and your authority will grow.
Question: Is a Cybersecurity Certification the Same as Security Clearance?
No. A cybersecurity certificate is issued by an authority of some kind in the cybersecurity space, such as:
- Cisco, a company specializing in networking hardware and software.
- CompTIA, the Computing Technology Industry Association.
- (ISC)2, the International Information System Security Certification Consortium.
- Isaca, the Information Systems Audit and Control Association.
- EC-Council, the International Council of Electronic Commerce Consultants.
These are all private bodies, not attached to a single government or country. They represent authorities in online security with membership across the country and around the world. Their authority stems from their experience and knowledge.|

By contrast, a security clearance is issued by the United States Department of State and represents trust and accountability with the government. A security clearance is required for some federal jobs, as well as jobs in the private sector working with government contractors such as Northrup Grumman, Booz Allen Hamilton, or IBM. A security clearance is only relevant if you’re looking to work as part of a government team or government contractor.
A cybersecurity certificate can still be useful or even necessary for roles in which a security clearance is required, but can help outside of those roles as well. If you had to pick one or the other, in general, you would want the cybersecurity certificate.
Question: Is a Kingsland University Degree the Same as a Cybersecurity Certificate?
We are not a certificate issuer. Our program is designed to educate you and prepare you to take and pass the Certified Ethical Hacker and Security+ certifications offered by various authorities, and to provide you with a rounded education in cybersecurity that includes both defensive and offensive tools, techniques, and knowledge. Our program does not award a certificate directly; rather, it educates you as well as prepares you to earn certificates by taking and passing the relevant tests.

These security tests are some of the most rigorous and difficult in the industry, and without the proper knowledge and education, it’s not likely that you’ll pass on your own. Certificates aren’t everything, though, which is why a well-rounded education is so important.
Question: What Cybersecurity Certificates Do You Offer?
Our cybersecurity program includes several modules, including:
- An introduction into the basics of cybersecurity, including cryptography.
- Network design, architecture, security, and scripting.
- Defensive security, including policy compliance, enterprise security, auditing, and analysis.
- Offensive security, including vulnerability overviews, system assessments, and ethical hacking.
- Threat analysis, modeling, and incident handling.
- Certification prep.
Our education prepares you to take tests to earn two kinds of certificates: the defensive Security+ certificate and the offensive Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) certificate. The knowledge you gain through the program can also transfer into general security certificates, and you will be able to earn a variety of other certificates through ongoing study, continued education, and exploration of the subject yourself.
Your Thoughts
Do you have a question we haven’t answered in this FAQ? If so, feel free to contact us. You can leave a question in the comments below for us to answer, or you can reach out to us through our contact form or via social media. We’re always happy to talk to prospective students and answer any questions you may have.


